Step 74 of 117
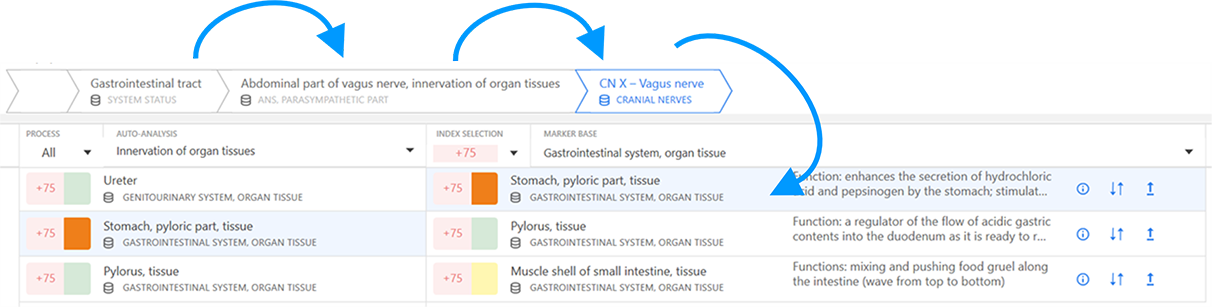
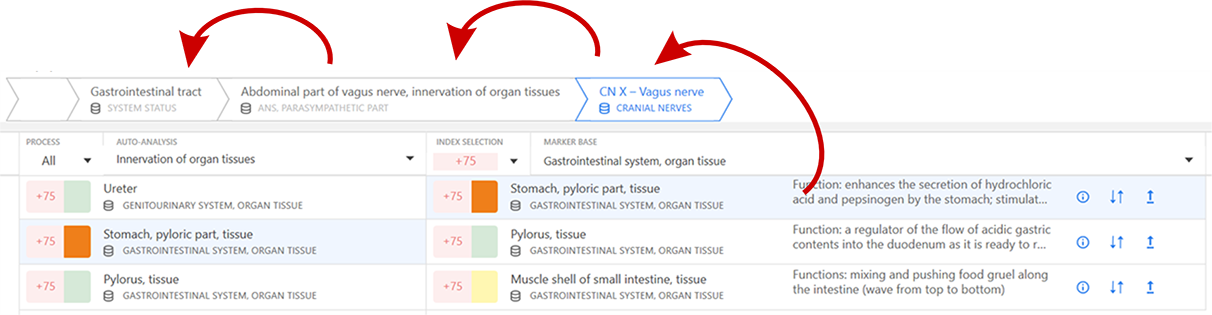
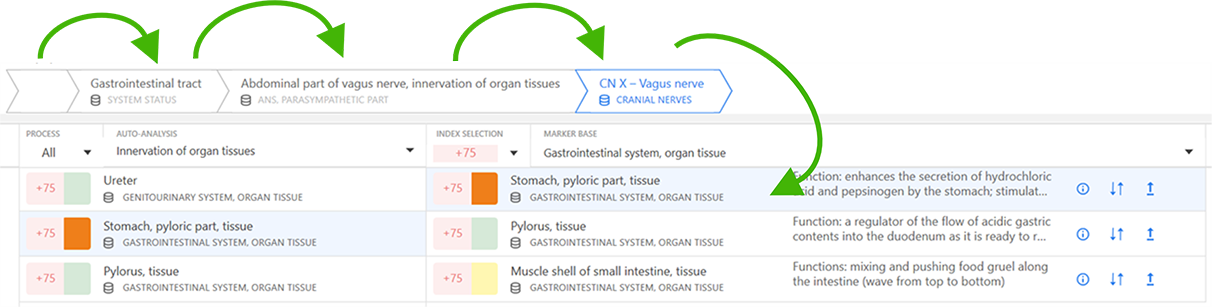
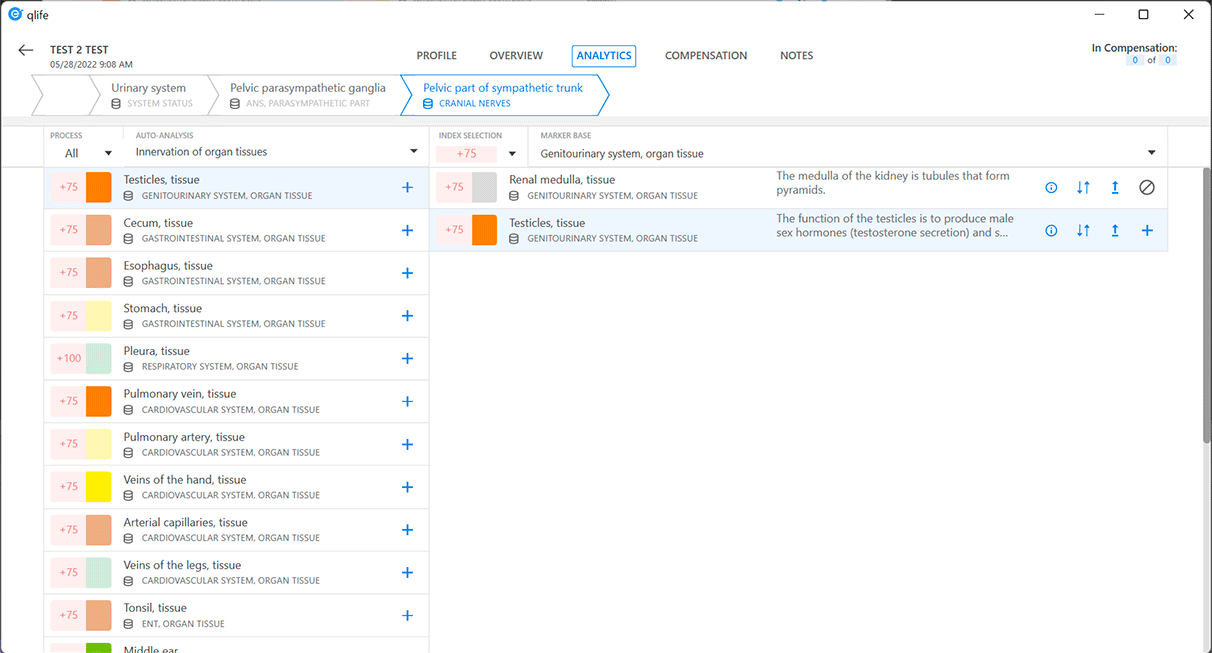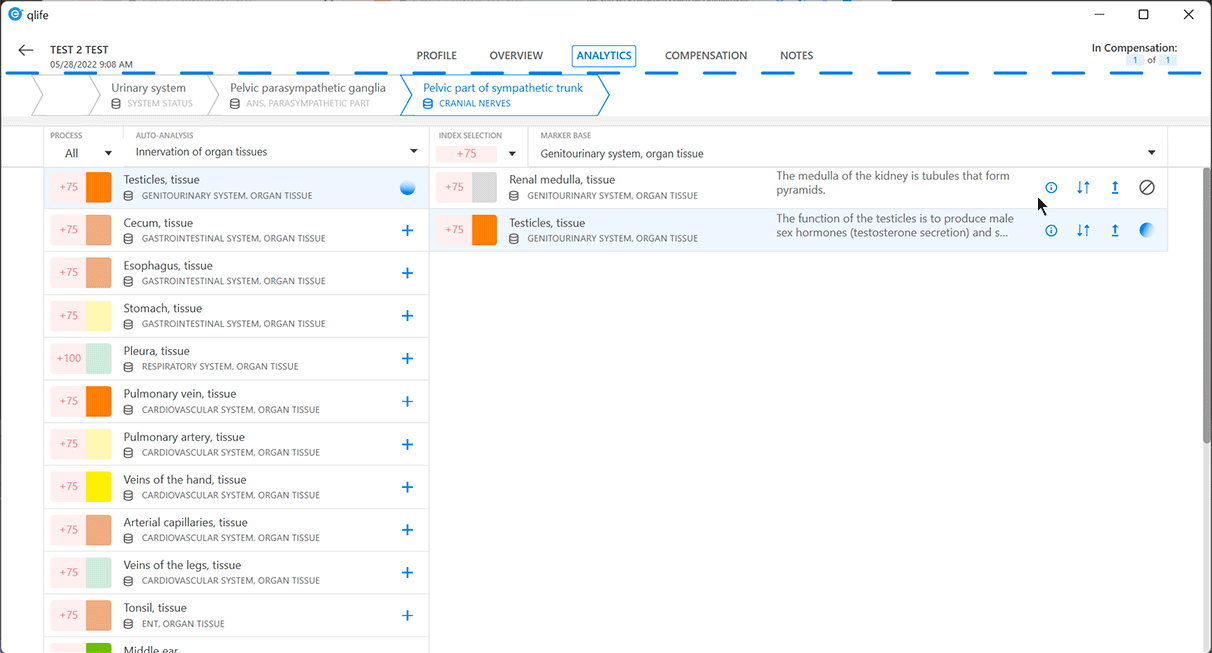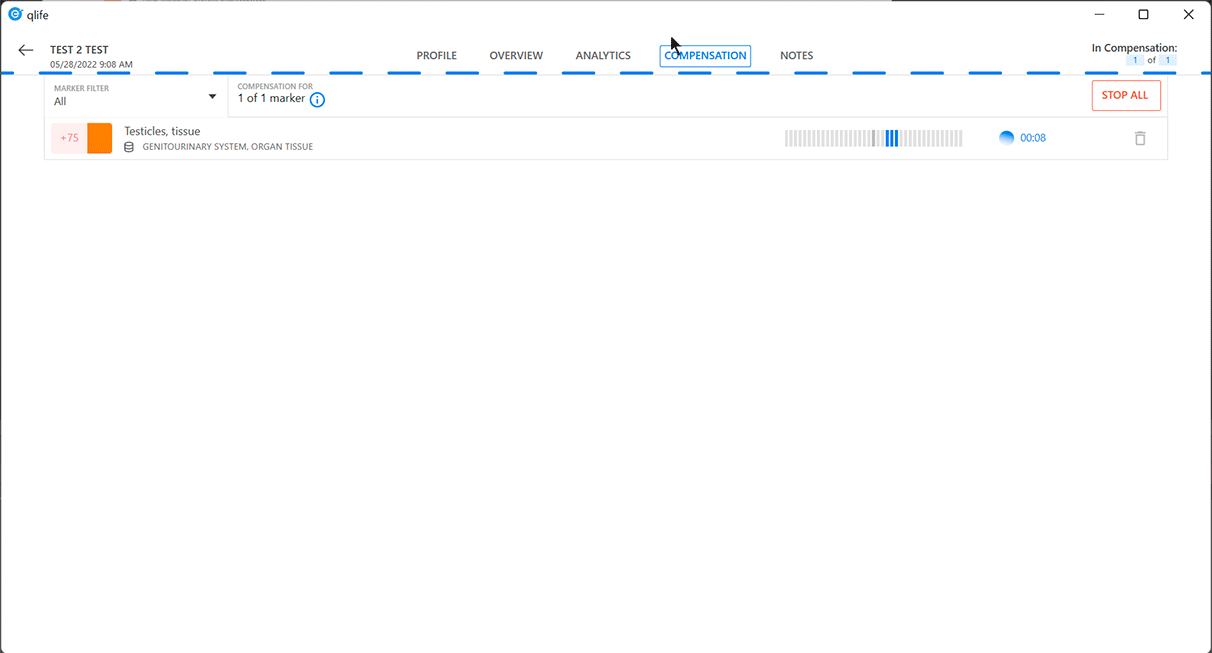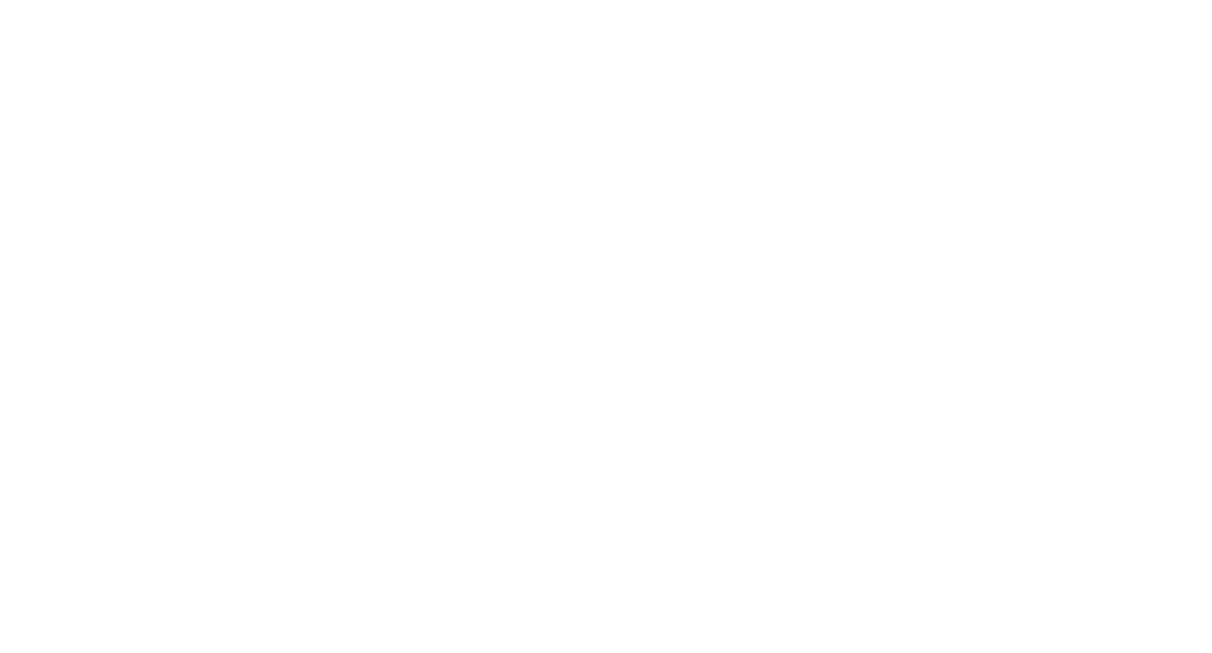
Auto-analysis chain
The "analysis chain" method is used in the "Analytics" window of the eri-Qlife application to describe the relationship of the processes to each other and to determine the causality relations of their states. This method is used both when performing an auto-analysis and building a sequence of relationships of their mutually influencing processes while analyzing them manually.
Next Exit